K8S – Utilisation de k8s sur Google Cloud
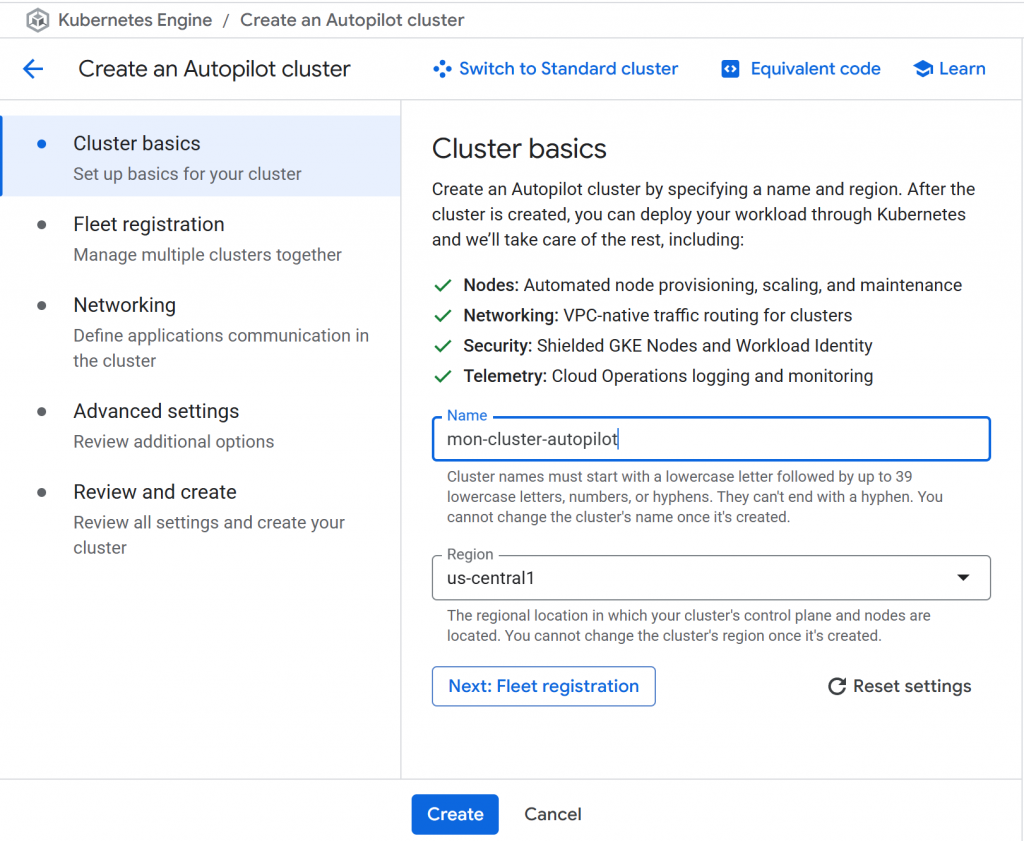
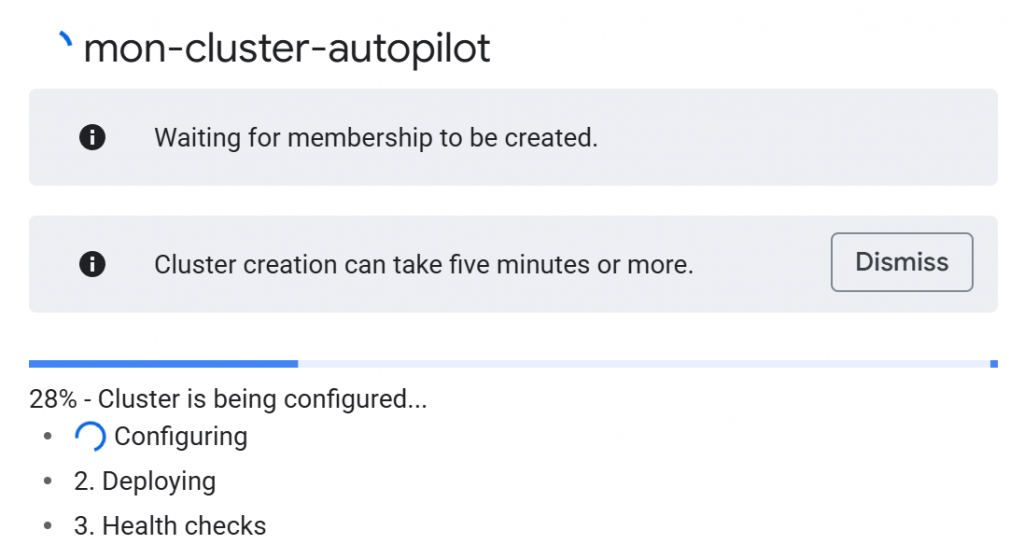
1 – Création d’un cluster (amas)
2 – Connexion au cluster via gcloud:
2.1 – Au besoin, installer gcloud
https://docs.cloud.google.com/sdk/docs/install?hl=fr
2.2 – Ouvrir Google cloud SDK shell
- Choisir un compte de login
- Choisir un projet
- Choisir une zone pour le traitement (1)
Ce qui devrait afficher le texte suivant:
The Google Cloud CLI is configured and ready to use! * Commands that require authentication will use alin.boudro@gmail.com by default * Commands will reference project `info420` by default Run `gcloud help config` to learn how to change individual settings This gcloud configuration is called [default]. You can create additional configurations if you work with multiple accounts and/or projects. Run `gcloud topic configurations` to learn more. Some things to try next: * Run `gcloud --help` to see the Cloud Platform services you can interact with. And run `gcloud help COMMAND` to get help on any gcloud command. * Run `gcloud topic --help` to learn about advanced features of the CLI like arg files and output formatting * Run `gcloud cheat-sheet` to see a roster of go-to `gcloud` commands.
2.1.2 – Tester l’installation de gcloud
gcloud cheat-sheet
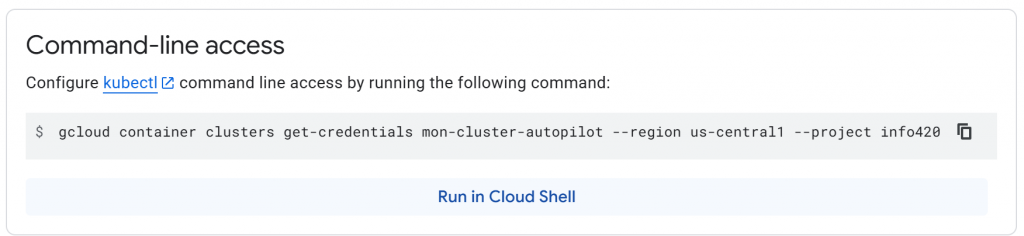
2.3 – Accès au cluster localement
gcloud container clusters get-credentials mon-cluster-autopilot --region us-central1 --project info420
En cas d’erreur, par exemple:
CRITICAL: ACTION REQUIRED: gke-gcloud-auth-plugin, which is needed for continued use of kubectl, was not found or is not executable. Install gke-gcloud-auth-plugin for use with kubectl by following https://cloud.google.com/kubernetes-engine/docs/how-to/cluster-access-for-kubectl#install_plugin kubeconfig entry generated for mon-cluster-autopilot.
Suivre le lien du message et installer le plugin manquant
gcloud components install gke-gcloud-auth-plugin
Après la correction, retourner au point 2.3
2.4 – Tester l’accès au cluster situé sur le cloud de Google
Z:\>kubectl get all NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE service/kubernetes ClusterIP 34.118.224.1 <none> 443/TCP 31m
2.5 – Tester avec un manifeste, à partir du fichier suivant:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment
labels:
app: nginx-123
spec:
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
mon-app: nginx-456
template:
metadata:
labels:
mon-app: nginx-456
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: alainboudreault/superminou:latest
imagePullPolicy: Always
ports:
- containerPort: 80
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx-service
spec:
selector:
mon-app: nginx-456
type: LoadBalancer
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 80
Dans un terminal, taper les commandes suivantes:
kubectl apply -f superminou.yaml kubectl get all kubectl edit deployment nginx-deployment # Augmenter les réplicats à 4 kubectl get all
Vérifier l’état du déploiement (section workload) dans la console de Google Cloud
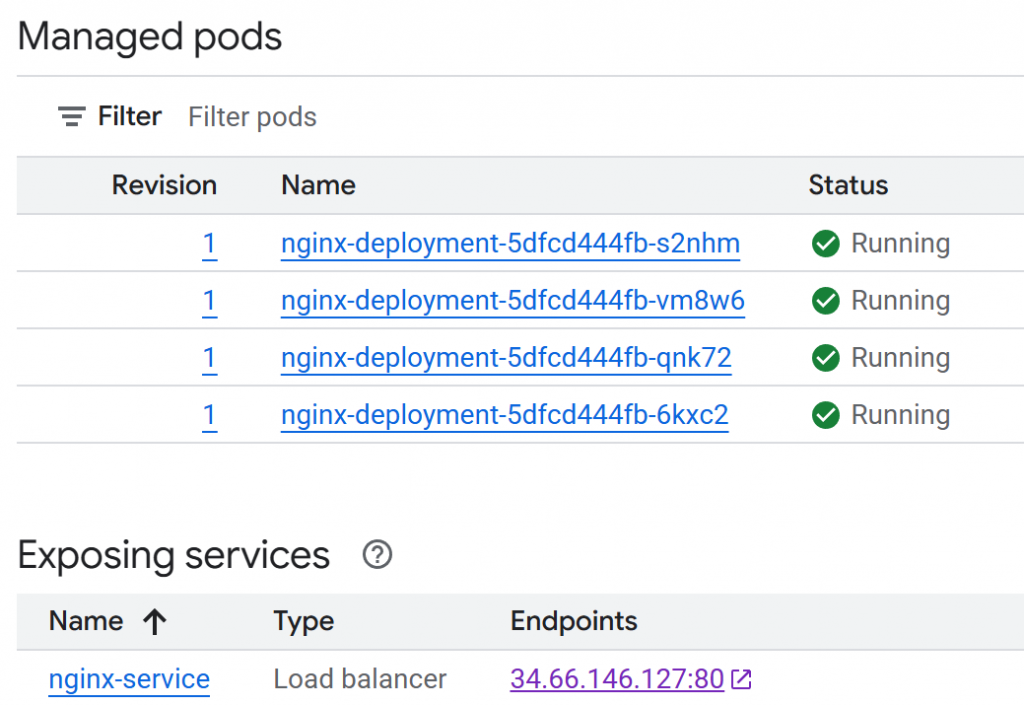
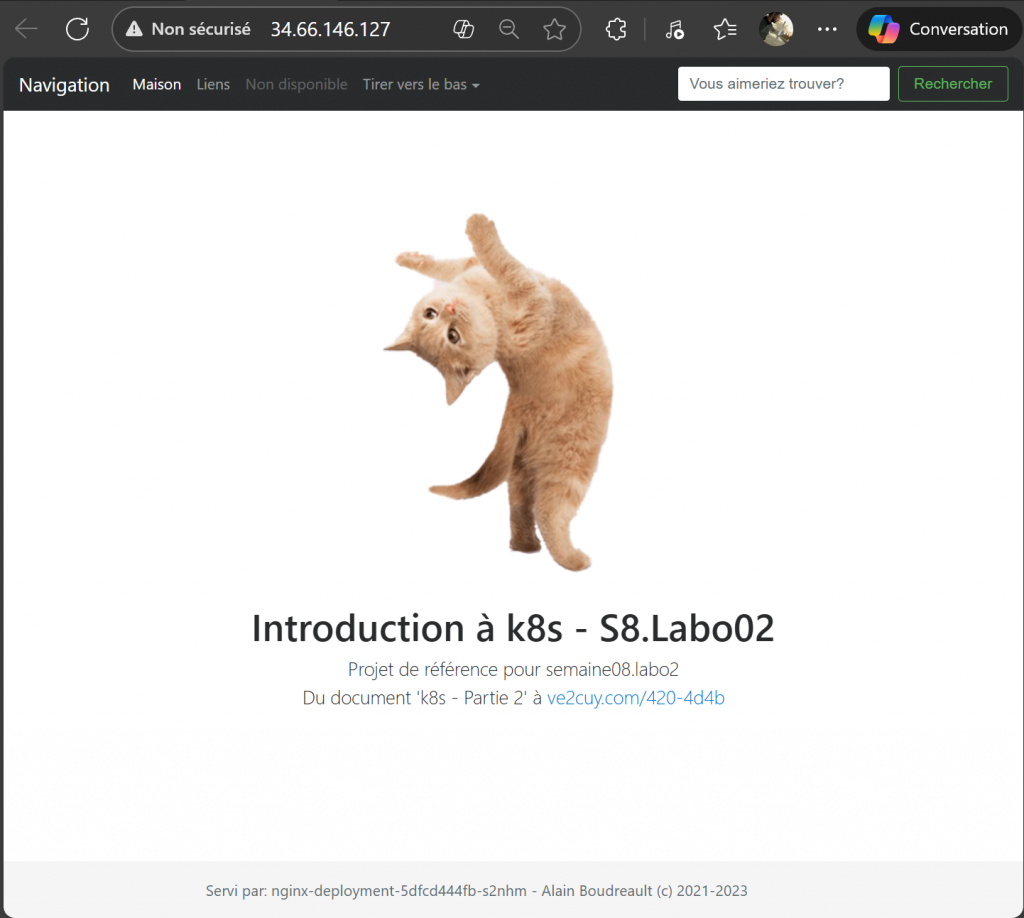
Le service de type ‘LoadBalancer’ devrait avoir reçu une adresse ip publique (EXTERNAL-IP):

Tester l’adresse dans un fureteur: