Installation de Docker
23 Décembre 2020

1 – Docker-Desktop
La façon la plus simple d’installer Docker sur un poste de travail est d’utiliser l’application d’installation de Docker-Desktop. Cette application est disponible pour Windows, Linux et MacOS.
La page de téléchargement est disponible à cette adresse:
Bien que cette application soit intéressante et simple à installer, parfois une version sans GUI est requise, par exemple, sur un serveur.
Ce document explique comment installer Docker à partir d’une CLI.
2 – Installation manuelle sous Ubuntu (Server ou Desktop)
// Mise à jour le 2025.10.24
// Au besoin, retirer le mot de passe sur sudo
sudo visudo
leNomUtilisateur ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL
// 1 - Effacer toutes installations précédentes
$ sudo apt remove $(dpkg --get-selections docker.io docker-compose docker-compose-v2 docker-doc podman-docker containerd runc | cut -f1)
// Faire la configuration de apt-get pour permettre l'ajout d'un nouvelle source via HTTPs
// Ajout du dépôt d'installation de Docker
# 2 - Ajouter la clé PGP officielle de Docker:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install ca-certificates curl
sudo install -m 0755 -d /etc/apt/keyrings
sudo curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg -o /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc
sudo chmod a+r /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc
# 3 - Ajouter le nouveau dépôt aux sources de 'apt':
sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.sources <<EOF
Types: deb
URIs: https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu
Suites: $(. /etc/os-release && echo "${UBUNTU_CODENAME:-$VERSION_CODENAME}")
Components: stable
Signed-By: /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc
EOF
sudo apt update
// 4 - Procéder à l'installation de Docker:
$ sudo apt install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io
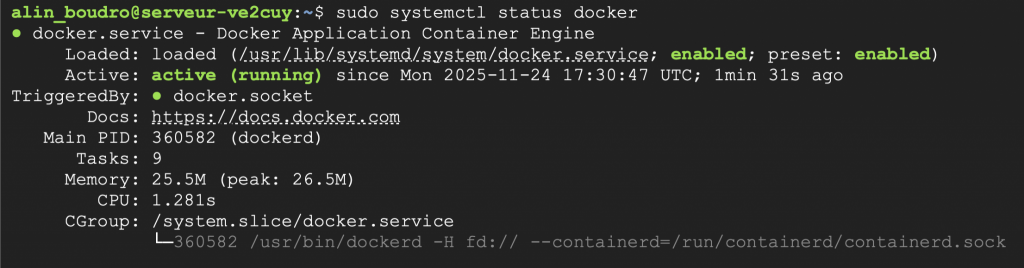
// 5 - Vérifier l'état du service:
sudo systemctl status docker
// 6 - tester Docker $ docker --version
2.1 – Configuration de Docker sans sudo
// 1 - Tester la commande suivante: docker run hello-world // Ça devrait produire l'erreur suivante:
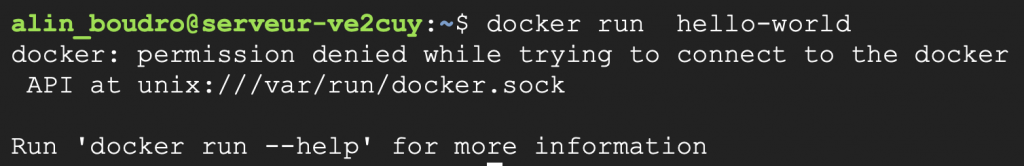
# Si le groupe docker n'est pas présent, il faut le créer grep docker /etc/group sudo groupadd docker # Ajouter l'utilisateur courant au groupe sudo usermod -aG docker $USER # Actualiser le changement au groupe docker newgrp docker # La commande suivante devrait maintenant fonctionner au niveau de l'utilisateur courant: docker run hello-world
3 – Installation sous Ubuntu avec Vagrant
Voir ici
4 – Installation sous Windows
Note: Si Docker-Desktop démarre de façon infinie alors il faudra peut-être installer (m-a-j) wsl:
wsl --update